Fortinet Acquires Next DLP Strengthens its Top-Tier Unified SASE Solution
Read the release

Cloud breaches increased by 75% from 2023 to 2024. As more organizations move to the cloud and embrace remote work, they need new ways of combating threats without compromising connectivity and productivity. This is where Zero Trust security comes into play.
Zero Trust security assumes no entity—whether inside or outside the network—is trusted as a default. Traditional security approaches assume everything inside an organization’s network is trustworthy, but that’s no longer secure enough.
A Zero Trust security framework verifies every request to access the network. This new model shifts the focus from guarding the perimeter to an identity-based approach, assuming every access request from any user, entity, device, or system is a potential risk, regardless of whether it comes from within or outside the network.
In this guide, we’ll explain what a Zero Trust security framework is, show why this approach is so beneficial, and share tips to help you implement Zero Trust security in your organization.
In this article:
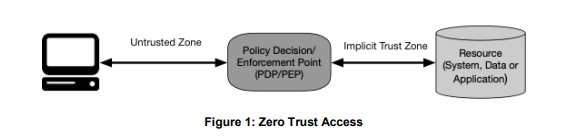
Zero Trust security, first developed in 2009, assumes no entity is automatically trustworthy. Instead, this model requires verifying every user, device, and application that attempts to access the network, ensuring that only authorized and authenticated entities can gain access.
The core philosophy of Zero Trust is “never trust, always verify.” In the past, “castle-and-moat” cybersecurity models relied on creating a secure perimeter, which allowed organizations to trust everything inside the network. This model only considered external entities as potential threats.
This approach worked well when organizations had their resources and workers on-premises. However, with the rise of cloud computing, sophisticated cyber threats have rendered this model obsolete.
Zero Trust security is the gold standard for the age of cloud computing and remote work. Instead of creating a secure perimeter, this approach secures every access point. This shift acknowledges that threats can come from inside and outside the network, making it essential to continuously verify all access requests.
Zero Trust is a multi-tiered approach to cybersecurity that follows several processes to keep your organization safe:
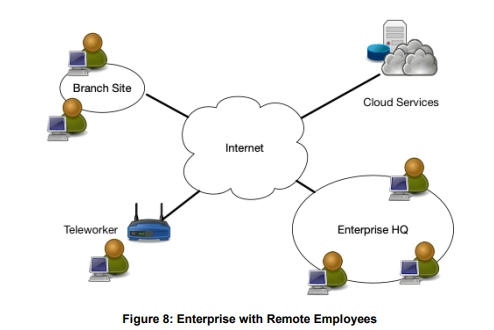
Zero Trust security is crucial for today's mobile workforce, addressing challenges like securing remote workers, hybrid cloud environments, and ransomware threats.
Organizations adopting Zero Trust security assume that they will be breached, a stance that's particularly relevant today. In fact, a 2023 survey conducted by Forrester found that 74% of organizations surveyed had experienced a data breach at least once within the previous year.
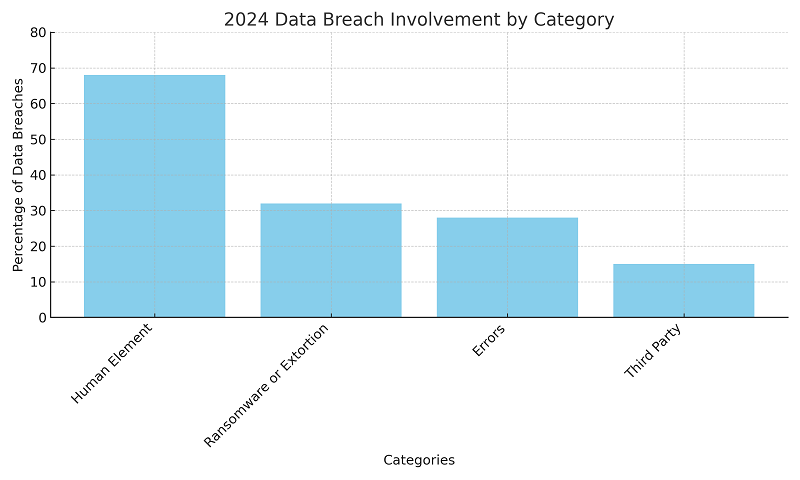
What's more, another survey found that "74% of IT decision makers surveyed whose organizations have been breached in the past, say it involved privileged access credential abuse," according to Forbes. And according to Verizon's 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report, among data breaches occurring within the past year:
The 15% of breaches involving a third party marks an increase of 68% from 2023, primarily driven by zero-day exploits used for ransomware and extortion.
The Zero Trust security framework requires all users, regardless of their location, to be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated before accessing applications and data. It replaces traditional VPNs, controls access for cloud environments, and streamlines onboarding processes.
By adopting a Zero Trust model, organizations can improve their security posture, reduce the risk of malware, and simplify architectural complexity in an increasingly distributed work environment.
Zero Trust security is particularly crucial for new IT deployments, especially those involving cloud environments. Implementing Zero Trust in complex networks requires a phased approach, dedicated teams, and careful planning.
This strategy is recommended by cybersecurity experts, such as the UK National Cyber Security Centre, for organizations planning significant use of cloud services.
The Zero Trust model involves granting authenticated users and devices tailored, siloed access to only the resources they need, regardless of whether these resources are on-premises or in the cloud. This approach offers numerous benefits, including enhanced protection of sensitive data, improved compliance auditing, reduced breach risk, and better control in cloud environments.
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud-based solutions and distributed networks, Zero Trust becomes essential for maintaining robust security in modern enterprise ecosystems.

Zero Trust frameworks are highly customizable, but they all follow these three main principles to ensure end-to-end protection.
Zero Trust security approaches require explicitly verifying every request to access your network. This involves using authentication methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA) to confirm the identity of users and devices before granting access. Verification is continuous to ensure that all interactions are authenticated and authorized.
Not all users require the same level of access to do their jobs. With the principle of least privilege, users and devices only receive the minimum level of access to perform a task. Least privilege minimizes potential damage from compromised accounts or devices because attackers have limited access to critical resources.
It might sound counterintuitive, but Zero Trust security assumes data breaches will happen. Instead of assuming breaches could never happen to your organization, this mindset promotes proactive security measures. Constant monitoring, rigorous access control, and swift incident response protocols help organizations prepare for and mitigate the impact of unexpected security incidents more effectively.
Castle-and-moat approaches just can’t keep up with today’s cyber threats. Implementing an agile Zero Trust framework offers more protection in this always-on threat landscape.
Zero Trust security is a proactive model that reduces your attack surface and makes it harder for cybercriminals to penetrate the network. At scale, this improves your security posture and better prepares you to fight against evolving cyber threats. You can’t prevent all potential attacks or breaches, but this approach is a significant improvement over more reactive castle-and-moat approaches.
Zero Trust security frameworks reduce the risk of breaches by continuously verifying user identities and device security. This principle ensures that only authorized users with a legitimate need can access your critical data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. By minimizing the risk of breaches, organizations can avoid the significant financial and reputational damage associated with data leaks and exfiltration.
Zero Trust also safeguards personal and financial information by vigorously vetting all access requests. This approach protects sensitive data, ensures business continuity, and maintains your reputation.
Zero Trust security helps you meet compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and more by enforcing strict access controls and continuous monitoring. Adhering to these regulations helps you avoid legal and financial penalties and demonstrates a commitment to protecting customer data.
Zero Trust security provides robust protection at every level of your organization. Both small businesses and large enterprises can tailor Zero Trust principles to fit their environments and requirements. Zero Trust frameworks are much more flexible than past frameworks, allowing your organization to adjust its security measures as it grows and changes.

Regardless of its size, your organization will benefit from moving away from reactive cybersecurity approaches and embracing a proactive Zero Trust framework. Follow these six tips to implement a Zero Trust security framework in your business.
Begin by assessing your current security measures. Look carefully at your current:
What are you doing well? Where are you falling short? Conduct a comprehensive audit to understand your organization's vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. Starting with your strengths and weaknesses will help you design a personalized Zero Trust framework tailored to your most pressing needs.
Once you understand your needs, develop a strategic plan outlining your Zero Trust security goals. This strategy should include a detailed roadmap for implementing Zero Trust, specifying key milestones and timelines.
Your strategy should also touch on the core components of Zero Trust security:
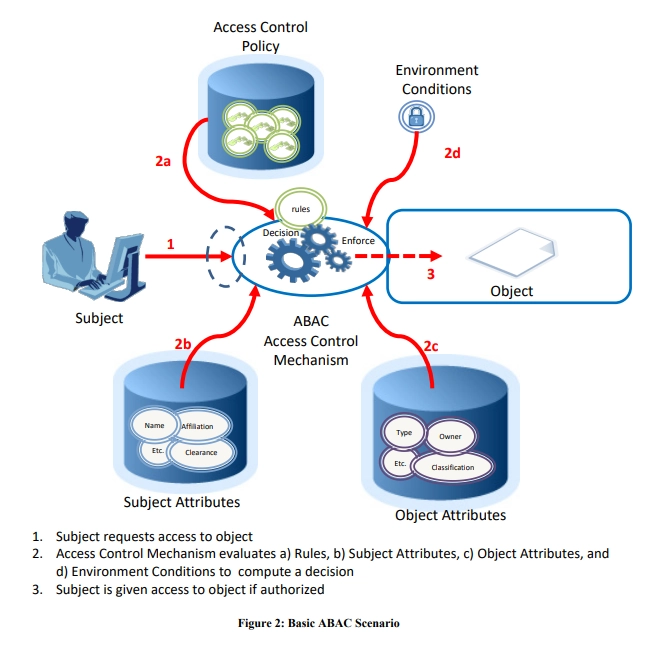
IAM solutions ensure only authenticated and authorized users access your network and resources. It includes:
Zero Trust security requires constant monitoring, not old-fashioned once-daily scans. Continuous monitoring and threat detection allow organizations to respond to security threats in real time, maintaining a vigilant security posture and minimizing potential damage from breaches.
Implement continuous detection by:
Zero Trust principles can only go so far. You also have to plan for the human element, which causes 74% of all breaches. Ensure all staff members understand and follow Zero Trust principles. This is the key to creating a culture of security awareness and reducing the risk of human error.
A cybersecurity-aware culture is key, but creating a culture of vigilance requires intentional effort. Follow these tips to empower your employees:
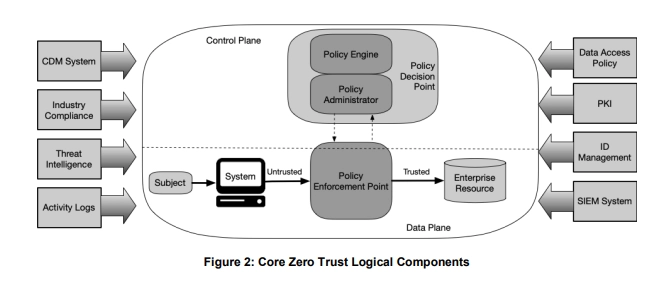
Some organizations implement Zero Trust with a patchwork of separate solutions and some consolidate all Zero Trust tools in a single platform. The consolidated setup simplifies cybersecurity by housing all resources in one place, granting unprecedented visibility into your network. The patchwork approach allows organizations to choose best-in-class products that may work best given the organization's requirements.
The Reveal Platform by Next is an industry-leading solution that provides data protection and insider risk tools and capabilities that play a part in a robust Zero Trust security strategy. The Reveal platform offers next-gen endpoint agents powered by machine learning to identify and categorize data at the point of risk (as it enters the environment), and employs behavioral analytics algorithms to identify normal vs. anomalous behavior.
Reveal also enforces your data handling policy and can automatically take preventive steps such as blocking the forbidden action or isolating an endpoint depending on the risk. Additionally, Reveal offers visibility into managed endpoints as well as unmanaged mobile devices, SaaS apps, USB drives, and printers—covering the many data egress points common in modern IT ecosystems.
Implementing a Zero Trust security framework is a critical step in safeguarding your organization against evolving cyber threats. By adhering to the core principles of Zero Trust, you can significantly enhance your security posture and protect sensitive data.
Implementation is often a hurdle for organizations, but the right tool makes all the difference. Leverage a comprehensive platform like Next Reveal to streamline the adoption and management of Zero Trust principles at scale. Request a demo now to see how Reveal streamlines Zero Trust security implementation.
Traditional security models rely on a secure perimeter and assume everything inside the network is trustworthy. In contrast, Zero Trust security doesn’t trust any entity by default, whether inside or outside the network. Zero Trust requires continuous verification and strict access controls for every access request.
The time required to implement a Zero Trust security framework varies depending on the size and complexity of the organization. Generally, it can take several months to a year to fully deploy Zero Trust principles.
While Zero Trust security emphasizes stringent access controls, that doesn’t necessarily hurt the user experience. User-friendly IAM solutions like single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) allow organizations to maintain strong security without burdening their users. The key is to balance security with convenience, ensuring that security measures don’t disrupt daily operations.

Blog

Blog

Blog

Blog

Resources

Resources
Resources

Resources
